Ruins of a Biblical city on a hill on the western end of Kziv creek. The site existed until the Crusaders and Mamluk periods, and preserved the Biblical name.

Home > Sites > Upper Galilee > Tel Avdon (Evron, Hebron)
Contents:
Background
Location
Structure
Aerial map
History
Photos
* Overview
* Eastern side
* Top of Tel
* South-East
Biblical
Etymology
Background:
Avdon (Evron or Hebron) is a hill on the western end of Kziv creek in the upper Galilee. An ancient site is located on the top of the hill. It is referred in the Bible, and existed from the early Bronze period until the Crusaders and Mamluk periods.
Joshua 19 24, 28: “And the fifth lot came out for the tribe of the children of Asher according to their families….And Hebron, and Rehob, and Hammon, and Kanah, even unto great Zidon;”
Location:
The Tel is located on the western end of the Kziv creek valley, in the upper Galilee. It is on the north bank of the creek. Its height is 146M, 70M above the creek.
The hill is 5KM east to the shore, exactly facing Tel Achziv (both have the same latitude).
You can access the site on foot from the south (from the road to the new settlement of Avdon), or from the east via (by a mountain trail that starts from the bridge above the Kziv creek). Both paths are difficult – no wonder the site was selected as a location for the fortified city. We have not yet tried the western side – it seems like an easier trail to walk up, but is a longer path.
Structure:
On top of the hill is the ancient city, and its size is 190M (west-east) by 120M. The ruins are located on its top and on the western hillside. The structures on the Tel are from different periods:
- Middle Bronze age – top of the Tel
- Iron age – top of the Tel and western hillside: fortifications; possibly the oil press on western side
- Persian/Hellenistic – western hillside
- Roman/Byzantine: Wall around the top of the hill; south-west structures
- Crusaders/Mamlukes – wall around the top, and structures on the top
On the south-western step of the Tel, within a structure, is a colorful mosaic floor. The mosaic has a geometric patterns, and it may be part of a church.
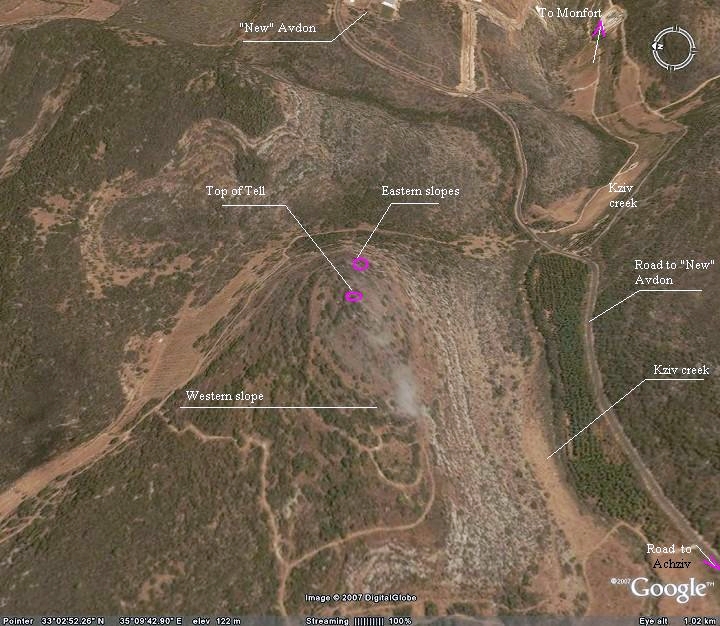
Aerial Map:
An aerial photo of Tel Avdon is shown below, taken in a Eastern orientation, and indicating the major points of interest.
History:
- Middle Bronze period – the birth of the city
According to the survey, the settlement on the hill started during the Middle Bronze age II (2000-1550BC). According to an article (Kabri survey), the lowland sites in this area during the first part of that period have declined and were replaced by the hilltop sites, such as Avdon, due to “a deterioration in the security situation”.
- Iron/Israelite period – Asher tribe
The city of Avdon continued through the Iron/Israelite period (1200-586 BC) and according to the Bible it was within the Asher tribe region, and one of the Levite cities. During this period the western fortifications were built. The site probably was destroyed (734-732BC) in the intrusion of Tiglath-Pileser III (Kings II 15: 29). This intrusion wiped out most of the Galilean sites, as written in the Bible.
- Persian/Hellenistic – resettlement
During the Persian and Hellenistic periods (5th-1stC BC) the site was resettled, perhaps by returnees. A large number of ceramics are located on the western hillside.
- Roman/Byzantine
The Romans and Byzantines built the impressive walls around the north and east side of the top of the hill, and the structures on the south-western side.
- Crusaders/Mamlukes
Avdon was a Crusaders site as well and is referred in a Crusaders document (1220) as part of the territory belonging to the one of the most noble Crusaders families – De Milly – whose center was in the nearby village Mei-liah (Mi’ilya) in the “Kings castle” (Castellum Regis”, also Mhlia). This family owned 36 villages and farms including the Montfort farm.
It is also listed in the sites that the Mamlukes permitted the Crusaders to keep during their last years (1260-1291).
- Modern times – the “New” Avdon
The site remained in ruins in the past 500 years. In 1952 a new settlement with the same name (the agricultural community of Moshav Avdon) was built 2 KM to the east, and first settled by Jews from Tunis and Iran.
In 1966 a major action movie was filmed on the west side of the hill. In this movie, “Judith“, the star actor was Sophia Loren. Remains of the set are located near the edge of the hillside. (During our visit to the site, a local Moshavnik I. Dan told us that the name Sophia is popular among the women of the Moshav…).
Photos
(a) Overview
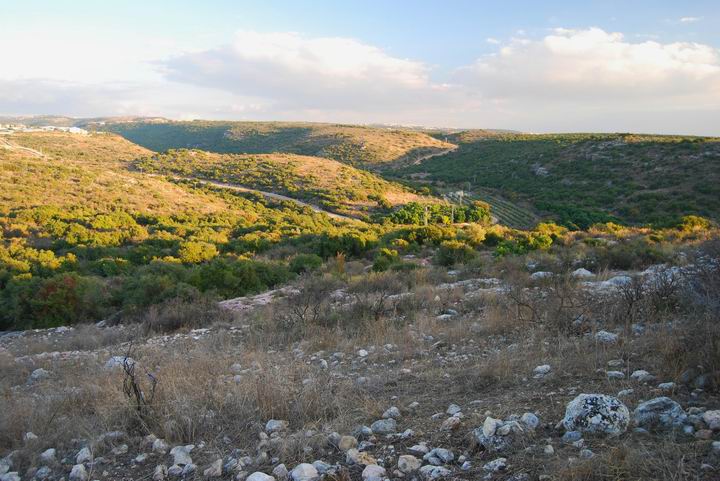
The photo below shows a southwest view of Tel Avdon, as captured by a quadcopter. The hill rises 70M above the Kziv creek with a very steep slope. Moshav Avdon is seen just behind the right side of the hill.
Click on the photos to view in higher resolution…
On top of the hill is a beautiful panorama of the Kziv creek valley, a 20KM long valley that starts from the western side of Mount Meiron. The photo below is the view towards the east. The “New” Avdon is seen on the left background.
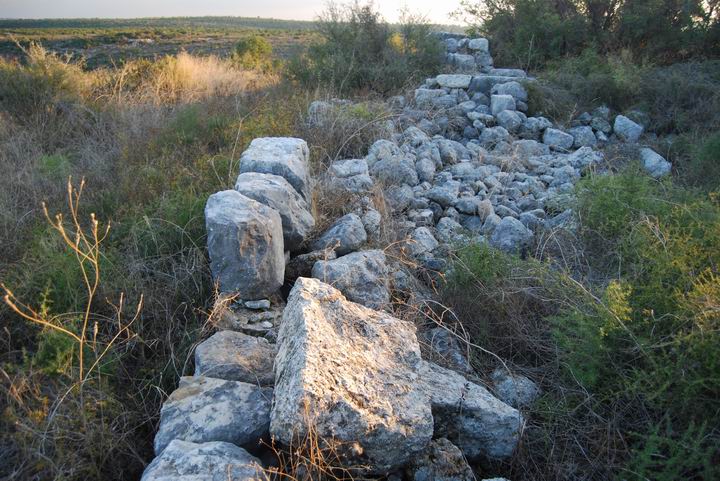
As seen on the photo, the eastern slope is covered by traces of ruins.
(b) Eastern slopes
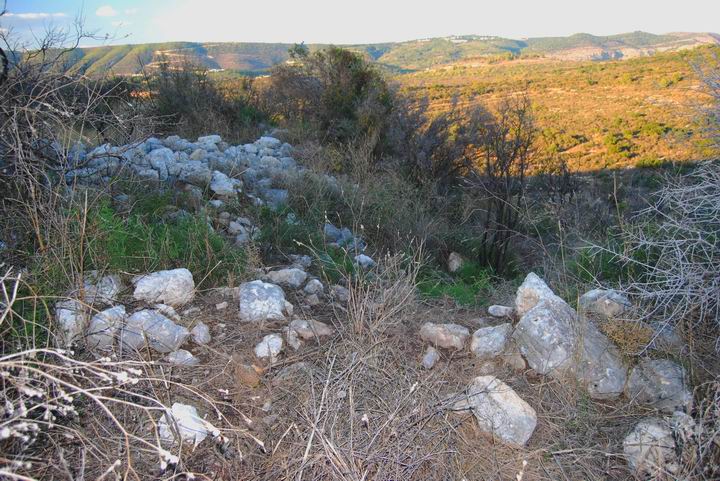
On the upper eastern hillside, close to the top, is a defensive wall, perhaps from the Roman and Byzantine period. It is located on the north and east side, about 20M from the outer walls of the structures at the top of the Tel.
The hill on the far background is the border with Lebanon. On the top of that hill, just south of the border, is Kibbutz Hanita.
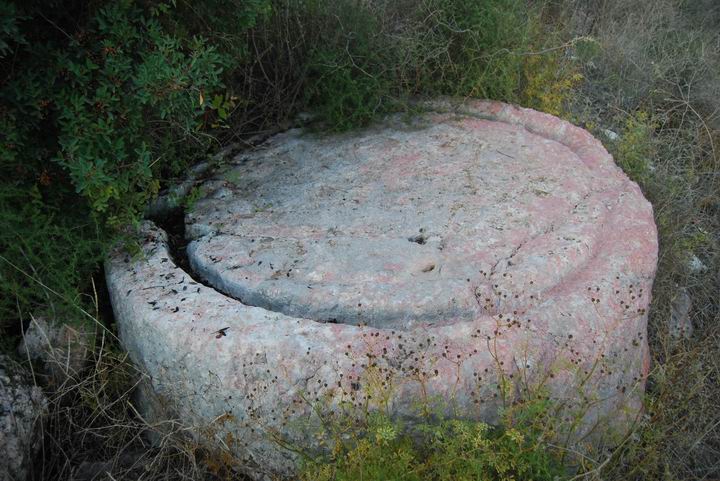
A press-bed of an oil press on the eastern slope. It is from the Byzantine period. According to the Oil presses guide
(Arch News XXXIV, page 56), this press-bed is of the type 4.2.2. This is how it worked: the olives were placed on the surface, and crushed by a stone (a 1.6M diameter stone, which is located nearby). Then the extracted oil collected into the grooves, flowed through the outlet on the left side into a collecting jar.
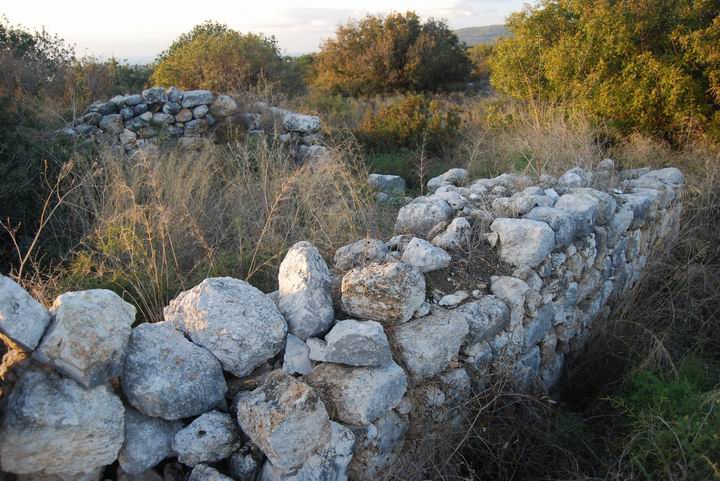
(c) Top of the Tel
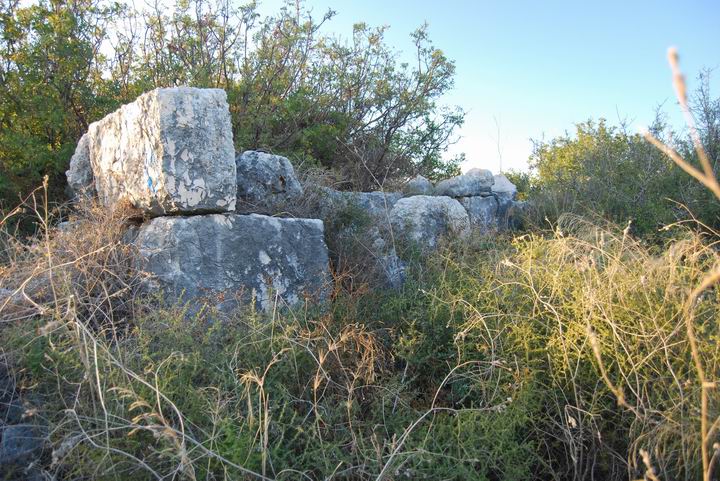
On the top of the Tel are the walls of about a dozen houses, arranged around a central yard in an area of about 45M by 40M. A wall surrounds the compound on all four sides. The hewn stones of these walls are from the later periods – Crusaders and Mamlukes.
Another view of the wall on the eastern side, looking towards the south (to Khirbet Suggar). The entire area is covered by thick array of bushes, making it hard to make an order of the structures in this area.
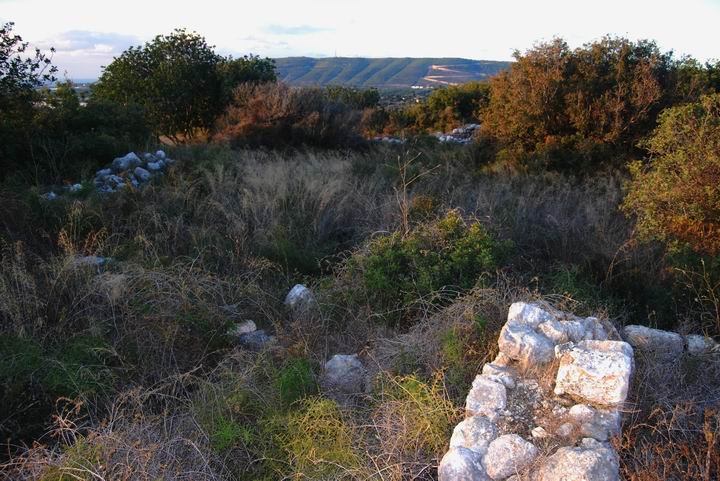
On the south-western side of the Tel, within one of the structures, is a mosaic floor. This structure may have been a church.
The western side is seen below, with the external wall that stretches along the west side. An opening in the external wall is located on the far side of the wall.
In the background is the northern border of Israel and Lebanon. The mountain is called Sulam-Tzor (“ladder of Tyre”). The Mediterranean sea, only 5KM to the west, is seen in the upper left corner.
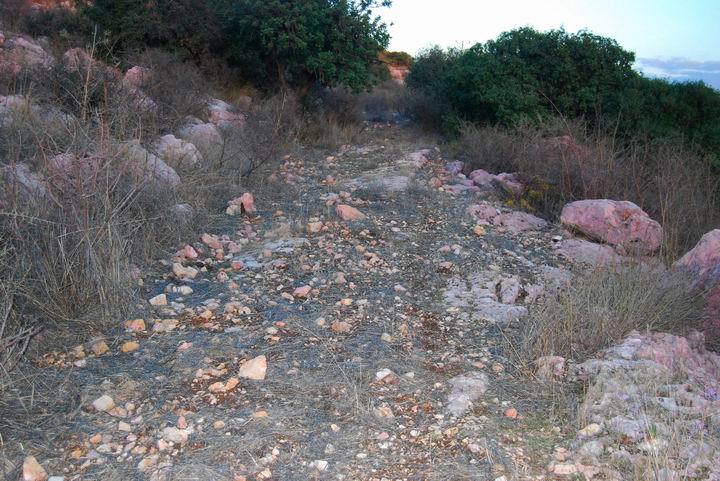
(d) South-East slope
A step on the south-east side of the Tel – may have been an ancient entrance road.
Note the color of most of the stones – they are tainted with a red color. Our reader, Steve Roth, provided an explanation for this red dye: “…the result of a chemical powder that the spray planes use to smother brush fires, it can hang around for a few years on the stones !”. Seems like a reasonable explanation – thanks!
Biblical References:
Joshua 19: 24, 28:
This text, describing the land of the tribe of Asher, lists the cities in their area and their border, and includes “Hebron”. The source Hebrew name is Evron, and was translated to “Hebron” in the KJV version. Some version have it as Ebron (NAS) or even Abdon (GW).
The Hebrew name in the Joshua text may have been a typo, since in other texts the name appears as “Avdon” (see below).
“And the fifth lot came out for the tribe of the children of Asher according to their families. And their border was …
… And Hebron, and Rehob, and Hammon, and Kanah, even unto great Zidon;”
Joshua 21: 3, 30:
Avdon was a Levite city. This tribe settled among the other tribe regions and had religious and political duties. In this text Avdon (Abdon) was listed as one of these cities, including the area around it:
“And the children of Israel gave unto the Levites out of their inheritance, at the commandment of the LORD, these cities and their suburbs…. And out of the tribe of Asher, Mishal with her suburbs, Abdon with her suburbs”
1 Chronicles 6, 74:
This text also lists Abdon as one of the Levites cities:
“And out of the tribe of Asher; Mashal with her suburbs, and Abdon with her suburbs,”
1 Chronicles 8, 23, 30:
There were two persons by the name of Abdon was listed in Benjamin’s family, and resided in Jerusalem and Gibeon. It was a common Hebrew name at that time.
“And Abdon, and Zichri, and Hanan,”
“And his firstborn son Abdon, and Zur, and Kish, and Baal, and Nadab,”
1 Judges 12 13-15:
Abdon was the 12th Judge:
“And after him Abdon the son of Hillel, a Pirathonite, judged Israel. And he had forty sons and thirty nephews, that rode on threescore and ten ass colts: and he judged Israel eight years. And Abdon the son of Hillel the Pirathonite died, and was buried in Pirathon in the land of Ephraim, in the mount of the Amalekites”.
Etymology (behind the name):
- Avdon (Abdon): from Hebrew, probably from the source name “Avad” which means worked, worshipped, enslaved, or served. The suffix “-on” is used in many names, and means in Hebrew “strong” or “forceful” or “son”, although in this context it may not have a meaning. Thus, the name may be translated as “the mighty worshipper” or ” servant”, of either God or the King. There were several distinguished persons in the Bible with this name, such as the 12th Judge, and the name of the city may have been called after this judge.
- Names of the Tel in different sources and maps preserved the ancient name:Rasabde (Teutonic Knights list of villages, 1220 AD), Khirbet Abdeh (French, 1891),A’bdeh (Guerin, 1880),’Abdeh (Conder and Kitchen SWP 1881),Abda (British map 1940).
Links:
-
Arch. Survey of Israel – Hanita Map (2) – R. Frankel & N. Getzov [1997] , site: #142.2
-
Arch. News XXXIV [1997] pp. 1-61: Oil presses in the Golan during the Mishna & Talmud periods
-
Wine & Oil Production in Antiquity in Israel & other Med. Countries [ISBN 1850755191 1998]Frankel, Rafael.
-
History & Technology of Olive Oil in the Holy Land [ISBN 09177526066 1994] Frankel, Avitson, Ayalon.
-
Kabri Regional Archaeological Survey Project [2006] Eric H. Cline and Assaf Yasur-Landau – This article reviews the MB period sites around Kabri, south of Avdon.
* Internal:
-
Quadcopter Aerial views – collection of Biblical sites from the air
BibleWalks.com – walk with us through the sites of the Holy Land
Monfort <<<–previous Upper Galilee site—<<<All Sites>>>—-next Upper Galilee site—>>> Masref
This page was last updated on Aug 8, 2014 (Added Aerial view)
Sponsored links:







