The mound is a Biblical city on the ancient Via Maris road, east to Acre, near Kibbutz Yasur.
Home > Sites > West Galilee >Tell Bira (Rehob/Rechob?)
Contents:
Background
Location
Aerial Map
History
Photos
* The Tell
* Oil press
* FlightOver
Biblical
Archaeological
Links
Etymology
Background:
The site is located on the route of the ancient road of Via Maris, the major highway that connect Egypt to Syria and the north.
Location:
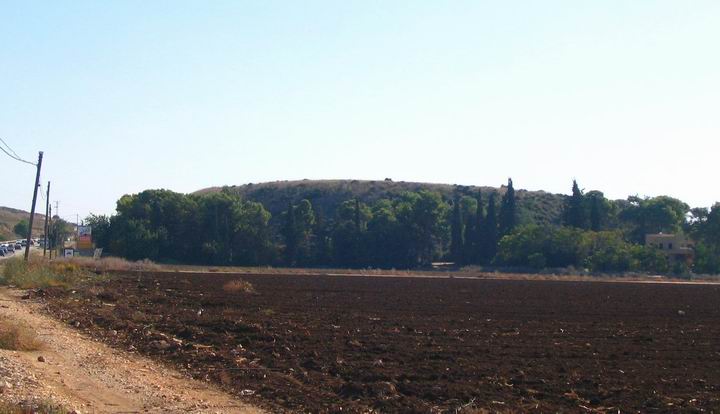
The Tell is located 8KM east of from Acre, on the modern road south from Akhihud junction. The road runs just a few meters from the eastern slopes of the Tell, which towers the road. On the east side of the road you can notice a small cave with tombs. The Tell is 51M above sea – about 30M above the valley around it, with almost vertical slopes.
An aerial photo of Tell Bira is shown below, indicating the major points of interest.
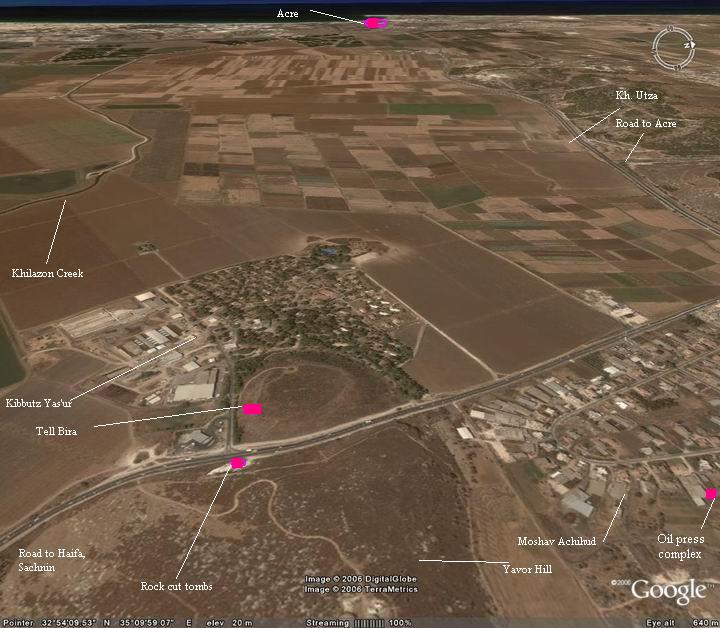
History of the place:
-
Bronze period thru Hellenistic period
The Tel was inhabited starting from the Early bronze period (3150-2200 BC). The ancient Canaanite builders used different measures to make their city more defendable: Massive walls, steep glacis, a dry moat. The city was probably based on a natural hill – the western ridge of the hill of Yavor. The valley between the hills, made out of a soft rock, was cut away to make the eastern side defendable.
There are also findings from later periods: Bronze period, Iron/Israelite age, Persian and Hellenistic (up to 4th century BC).
Biblical Identification:
It is identified as Biblical Rehob, which is listed by Joshua as one of the cities in the region of the tribe of Asher. Another identification may be Mishal, which is one of the 119 cities that Thutmose conquered in the 15th century BC.
The following text, describing the land of the tribe of Asher, lists the cities in their area. Note that the eastern border shifted eastwards after Solomon’s pact with Hiram, on the expense of Naftali. (Joshua 19:24-30):
“And the fifth lot came out for the tribe of the children of Asher according to their families….And Alammelech, and Amad, and Misheal; and reacheth to Carmel westward, and to Shihorlibnath; … And Hebron, and Rehob, and Hammon, and Kanah, even unto great Zidon…”.
The cities and roads during the Canaanite and Israelite periods are indicated on the Biblical Map below. Tell Bira is suggested on this map as Mishal.
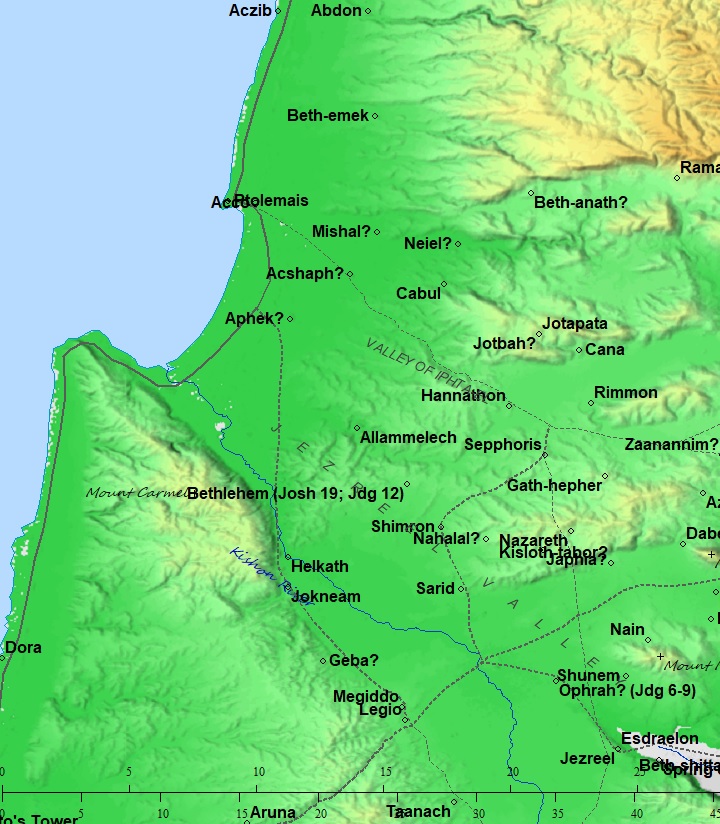
Map of the area around Tell Bira – during the Canaanite and Israelite periods (based on Bible Mapper 3.0)
-
Hellenistic period through Roman/Byzantine periods
During the Hellenistic period a new site was established on the north-eastern side of the Tell, in the fields of Moshav Achihud. The village flourished during the Roman/Byzantine period, and a large oil press was recently (2008) excavated in the site, perhaps part of a Byzantine monastery.
-
Modern periods
The Tell is in ruins for over 2000 years. A Kibbutz, Yas’ur, was established on the west side of the Tell in 1949. A Moshav, Achihud, was established in 1950 and is located several hundred meters north-east to the Tell.
Photos:
(a) Tell Bira:
An aerial view, captured by a quad copter, shows the top of the mound from its north. On the left is the highway that crosses the east side of the mound. In the background is the valley of the Hilazon brook, which flows from the left (east) side, towards the sea on the west (right side). On the right are the houses of Kibbutz Yas’ur.
Click on the photo to view it in higher resolution…
The following photo is a view from the ground level on the north side. The Tell is in the center, and the new road passes on the left side. At the right side is one of the houses of Kibbutz Yas’ur.
The next photo shows the eastern slopes of the Tell, and the main road that passes near its edge. In the background – the road from Acre (towards the left side) and Karmiel.
On the side of the road you can notice rock-cut tombs. Above the tombs is the hill of Yavor, an agriculture seeds research farm.
(b) Khirbet Achihud:
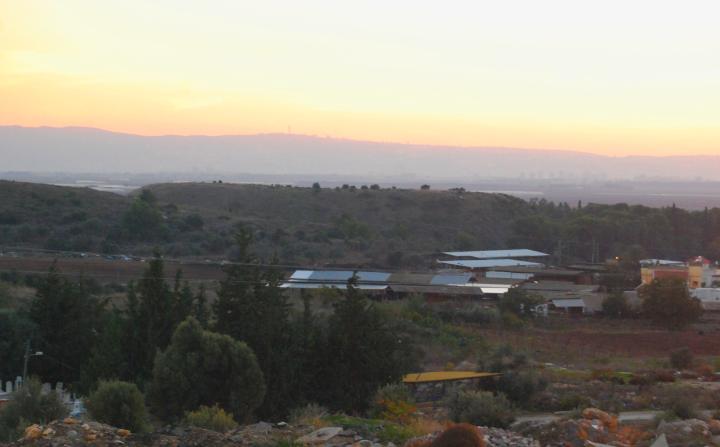
During the Hellenistic period, the Tell “died”, as it happened to all other ancient cities. A new village was established on the north-east side of the Tell, now located in the fields of the agriculture village of Achihud (Ahihud). The photo below shows the view from Achihud towards Tell Bira, with Mount Carmel in the background.
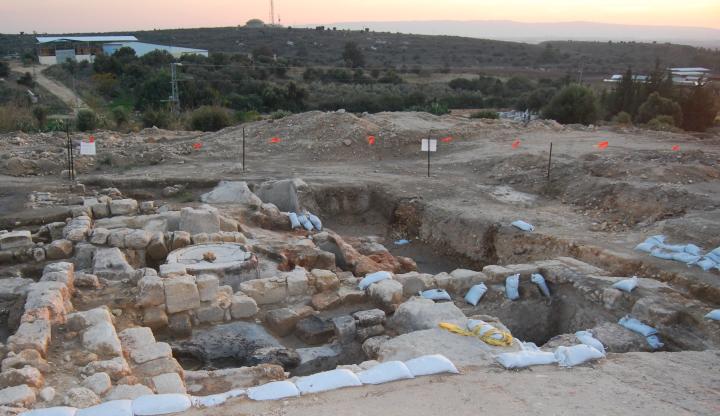
In 2008 a massive complex for producing oil, dated to the 6th-7th C Byzantine period, was excavated in the south-eastern side of Moshav Achihud.
The oil press complex is one of the largest in Israel. This production complex was based on a single crushing stone & basin and a triple set of oil presses. Most of the oil production sites used a single or double set of oil presses, but this site is based on three presses.
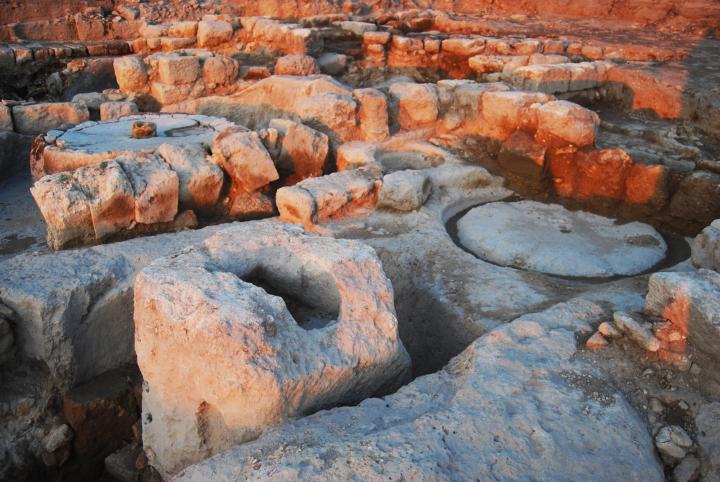
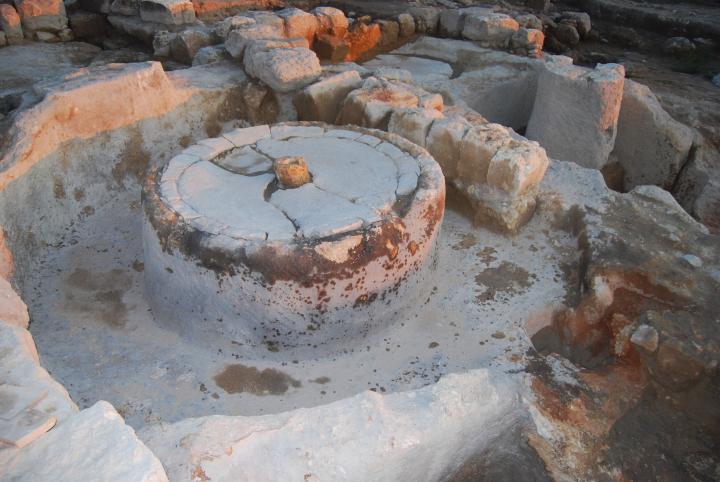
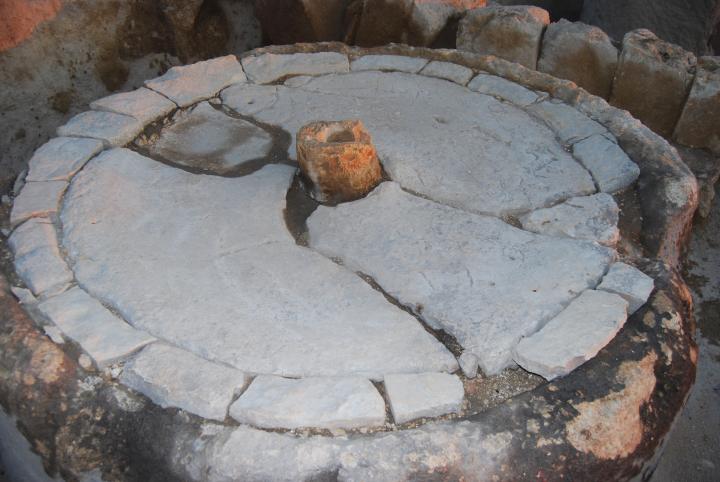
In the center of the complex is the basin of the crushing mill, seen below. Upon the basin was a heavy crushing stone that was turned by an animal, crushing the olives – the first step in the process of producing the olive oil.
A closer look at the crushing basin:
The crushed olives were then collected into baskets, and pressed by a second device in order to extract their oil. Three screw type press beds and a stone weight were found in the excavations.
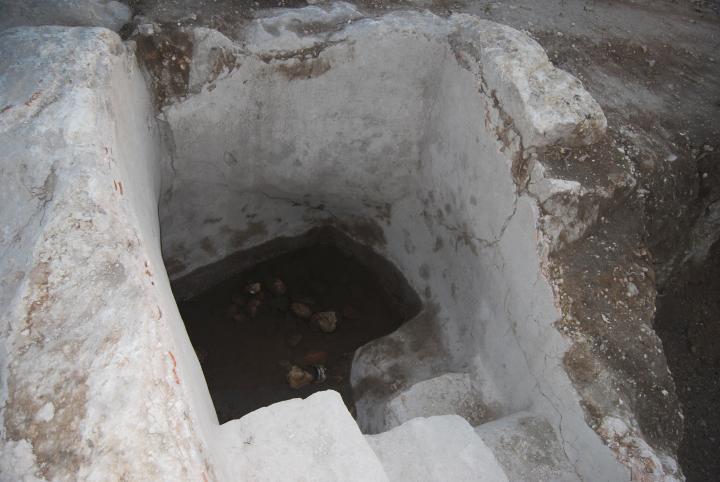
The oil would flow into a small pool, seen below. The stairs were used enable the workers to access the bottom of the pool, collecting the juice into jars.
Among the items unearthed in this emergency excavation were numerous roof tiles, fragments of plates, marbles and lamps. The archeologists relate the items to a nearby church, and they hypothesize that the oil press was part of a monastery.
(f) Flight over Tel Bira:
![]() An aerial view of Tell Bira can be seen in the following Youtube video.
An aerial view of Tell Bira can be seen in the following Youtube video.
Biblical References:
According to the biblical texts and the archaeological survey, Tell Bira is identified as Biblical Rehob. Assuming that it was indeed Rehob, there are several references to this city, as listed below. Note that there are other cities in Israel that are also called Rehob, and several of them are located in the Galilee. The reason for this was the name means in Hebrew “road”, and these cities were close to main roads.
(a) Joshua 19:24,25
This text, describing the land of the tribe of Asher, lists the cities in their area. One of the sites may relate to Tell Bira – it is to be Rehob. Joshua lists 2 such cities, one near Tyre and the other near Akko (Ummah) and Afek, which are in the vicinity of Tell Bira:
“And the fifth lot came out for the tribe of the children of Asher according to their families. And their border was Helkath, and Khali, and Beten, and Achshaph And Alammelech, and Amad, and Misheal; and reacheth to Carmel westward, and to Shihorlibnath; And turneth toward the sunrising to Bethdagon, and reacheth to Zebulun, and to the valley of Jiphthahel toward the north side of Bethemek, and Neiel, and goeth out to Cabul on the left hand, And Hebron, and Rehob, and Hammon, and Kanah, even unto great Zidon; And then the coast turneth to Ramah, and to the strong city Tyre; and the coast turneth to Hosah; and the outgoings thereof are at the sea from the coast to Achzib: Ummah also, and Aphek, and Rehob: twenty and two cities with their villages”.
(b) Judges 1: 31
However, due to the might of the city, Asher could not (initially) drive away the Canaanite inhabitants of Rehob. It is not clear which Rehob (near Tyre or this city), although the Rehob is mentioned after Aphik which is close to Tell Bira (7KM south).
“Neither did Asher drive out the inhabitants of Accho, nor the inhabitants of Zidon, nor of Ahlab, nor of Achzib, nor of Helbah, nor of Aphik, nor of Rehob“
(c) Joshua 21: 30-31
After the city was finally captured by the Israelites, Rehob became a Levite city. The Levy tribe settled among the other tribe regions and had religious and political duties. In this text Rehob was listed as one of these cities in the region of the tribe of Asher, including the area around it:
“Then came near the heads of fathers’ houses of the Levites unto Eleazar the priest, and unto Joshua the son of Nun, and unto the heads of fathers’ houses of the tribes of the children of Israel; and they spoke unto them at Shiloh in the land of Canaan, saying: ‘The HaShem commanded by the hand of Moses to give us cities to dwell in, with the open land thereabout for our cattle.’ And the children of Israel gave unto the Levites out of their inheritance, according to the commandment of HaShem, these cities with the open land about them”.
…
“And out of the tribe of Asher, Mishal with the open land about it, Abdon with the open land about it; Helkath with the open land about it, and Rehob with the open land about it; four cities”.
(d) 1 Chronicles 6:65
The Levite city was also listed in Chronicles:
“…And Hukok with her suburbs, and Rehob with her suburbs:”
Archaeological References and Links:
Tell Bira:
-
Carta’s Atlas of the Bible – Y. Aharoni [Carta Jerusalem 1974] – Shop for this must-have book.
Maps: 68, 108
-
Excavation (2007) – excavated buildings from the Middle Bronze age
Achihud:
-
Achihud Oil press excavation (2008) – press release
-
Large olive press discovered
* Internal links:
- Quadcopter Aerial views – collection of Biblical sites from the air
Etymology (behind the name):
- Tell, Tel – a layered mound (read about the story of the Tells)
- Bir – Arabic: well.
- Tell El-Bir El-Alarabi – The name of the Tell In Arabic: the West well (the east well was a village near Mt Tabor)
- Rehob – in Hebrew: Road. There are several such cities in biblical Israel, most of them are located near major roads.
- Yas’ur – name of the Kibbutz west of the Tell; in Hebrew: Albatross bird. Established 1949.
- Yavor – name of the agriculture farm east of the Tell; in Hebrew: select (the seeds) – the purpose of the farm.
- Khilazon – name of the creek that flows near the Tell. In Hebrew: snail; named after the purple color manufacturing industry that was based on the snail. It also implies a winding form of the creek.
BibleWalks.com – walk with us through the sites of the Holy Land
Tell Kisson <<<–previous site—<<<All Sites>>>—next West Galilee site–>>> Afek
This page was last updated on Oct 1, 2022 (add identification and Biblical map)
Sponsored links:






